|
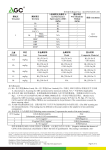
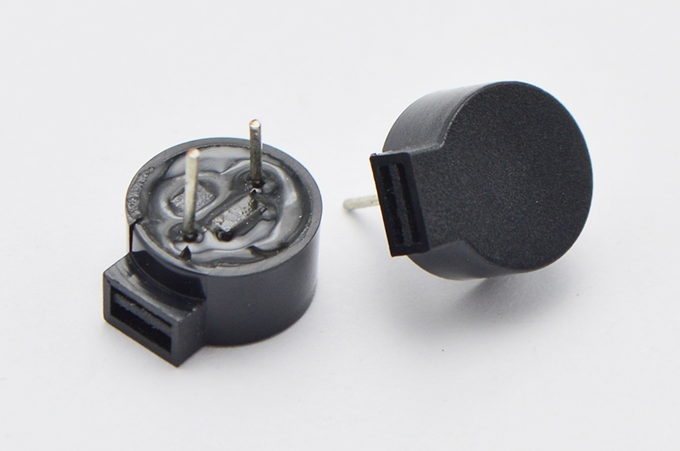
Piezoelectric microphone/buzzerA piezoelectric microphone/buzzer is a sound component made by mounting a piezoelectric vibrating plate in a plastic box. Piezoelectric microphones are sound components that can produce sound suitable for use as an input signal without the need for built-in oscillation circuitry. This feature allows them to be used in a wide range of applications. They are SMD type, suitable for small, high-density installations, while the pin type can be used for general purposes. Piezo buzzers are sound components that can be generated monotonically using a built-in oscillation circuit. The two most common technologies used in buzzer design are magnetic and piezoelectric. Many applications use either electromagnetic buzzers or piezoelectric buzzers, but the decision about which of the two technologies to use is based on many different constraints. Electromagnetic buzzers operate at lower voltages and higher currents than piezoelectric buzzers, while piezoelectric buzzers typically have a higher sound pressure level capability than electromagnetic buzzers. buzzer. However, it should be noted that the larger SPL provided by piezoelectric buzzers requires a larger footprint.
In an electromagnetic buzzer, an electric current is driven through a coil to produce a magnetic field. When current is present, the flexible iron disk is attracted to the coil, and when current is not flowing through the coil, the flexible iron disk returns to its "resting" position. The movement of the iron disk produces the sound from the magnetic buzzer, similar to the way a cone in a loudspeaker produces sound. Electromagnetic buzzers are current-driven devices, but the power source is usually voltage. The current through the coil is determined by the applied voltage and the impedance of the coil. Piezoelectric buzzers are used in applications similar to electromagnetic buzzers. Piezoelectric buzzers are constructed by placing electrical contacts on two sides of a disc of piezoelectric material and then supporting the disc on the edge of the housing. When a voltage is applied between the two electrodes, the piezoelectric material is mechanically deformed as a result of the applied voltage. This movement of the piezoelectric disk within the buzzer produces sound in a manner similar to the movement of the iron disk in the magnetic buzzer or speaker cone described above. A piezoelectric buzzer differs from an electromagnetic buzzer in that it is driven by voltage rather than current. A piezoelectric buzzer is modeled as a capacitor, while an electromagnetic buzzer is modeled as a coil in series with a resistor. The frequency of the sound produced by electromagnetic and piezoelectric buzzers can be controlled over a wide range by the frequency of the signal driving the buzzer. The piezoelectric buzzer exhibits a reasonably linear relationship between the input drive signal strength and the output audio power, while the audio output of the electromagnetic buzzer decreases rapidly as the input drive signal decreases. |